The Power of Vision Therapy: Clearer Vision and Brighter Futures

Read time: 5 minutes
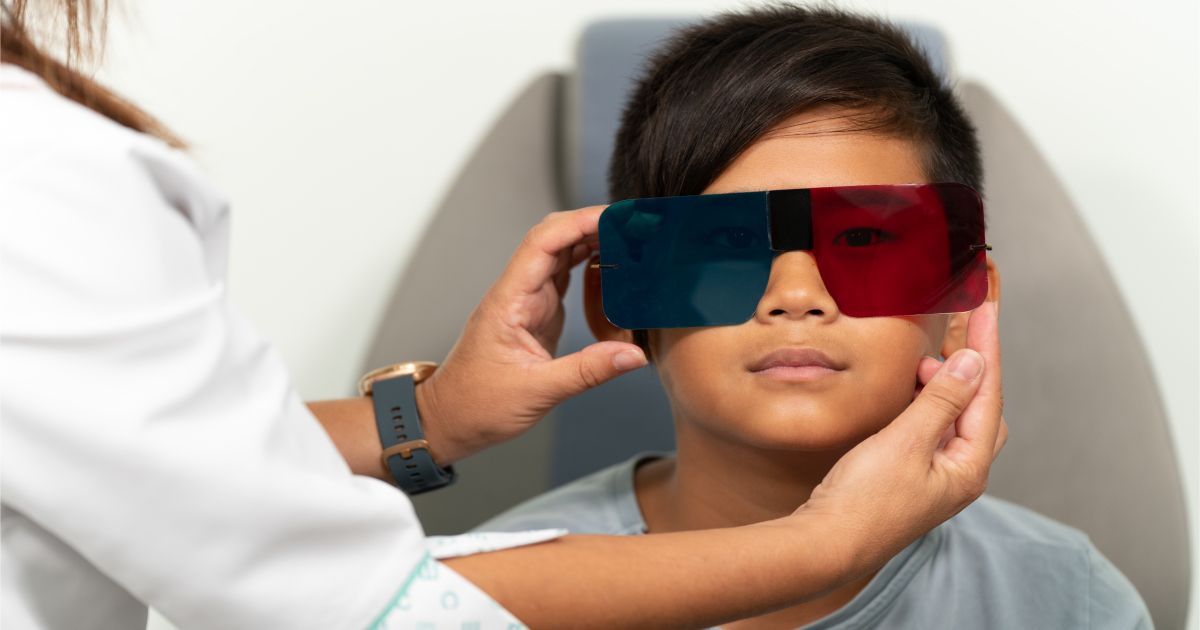
Are you familiar with vision therapy? In optometric care, vision therapy stands out as a specialized approach to addressing various visual conditions. Unlike traditional eyeglasses or contact lenses, vision therapy involves a series of exercises and activities designed to improve visual function and coordination. Let’s look at the world of vision therapy, discussing its different types, the conditions it can address, and the benefits it offers to patients seeking improved visual abilities.
Understanding Vision Therapy
Vision therapy, also known as visual training or orthoptics, is a non-surgical treatment option that aims to improve the way the eyes and brain work together. It is particularly beneficial for individuals with vision problems that cannot be fully corrected with glasses or contact lenses alone. By targeting specific visual skills, such as eye tracking, focusing, and coordination, vision therapy helps patients enhance their overall visual performance.
Among the diverse range of conditions that can be effectively treated with vision therapy are:
- Strabismus: Also known as crossed eyes, strabismus is a condition characterized by misaligned eyes. Vision therapy can help improve eye alignment and coordination, reducing the need for surgical intervention in some cases.
- Amblyopia: Commonly referred to as lazy eye, amblyopia occurs when one eye has significantly reduced vision compared to the other. Vision therapy, combined with patching or other treatments, can help stimulate visual development in the weaker eye.
- Convergence Insufficiency: Convergence insufficiency is a condition where the eyes have difficulty working together when focusing on nearby objects. Vision therapy exercises can strengthen the eye muscles and improve convergence abilities.
- Accommodative Disorders: Accommodative disorders involve difficulties with focusing, particularly during near tasks. Vision therapy can help individuals overcome problems such as accommodative spasm or insufficient focusing ability.
- Visual Processing Disorders: Visual processing disorders affect how the brain interprets visual information. Vision therapy aimed at improving visual perception can benefit individuals with conditions like dyslexia, ADHD, or developmental delays.
History of Vision Therapy
Vision therapy has roots dating back to the early 20th century when optometrists began exploring non-surgical methods to address certain visual conditions. One of the pioneers in this field was Dr. Frederick W. Brock, who introduced orthoptics as a method to treat binocular vision disorders in the 1920s. Orthoptics focused on exercises to improve eye coordination and alignment, laying the foundation for modern vision therapy.
In the 1940s and 1950s, Dr. Martin H. Birnbaum further advanced the field by developing techniques to treat amblyopia (lazy eye) and strabismus (crossed eyes) through vision training exercises. His work paved the way for the widespread adoption of vision therapy as a viable treatment option for various visual conditions.
Throughout the latter half of the 20th century, vision therapy continued to evolve, incorporating insights from neuroscience and behavioral optometry. The development of new technologies and methodologies expanded the scope of vision therapy, allowing for more targeted and effective interventions.
Today, vision therapy is recognized as a specialized branch of optometric care, offering personalized treatment plans for individuals of all ages with a wide range of visual challenges. Optometrists who specialize in vision therapy undergo extensive training to assess and address the underlying visual issues affecting their patients.
Contemporary vision therapy programs utilize a combination of traditional exercises, computer-based activities, and specialized equipment to improve visual function. These programs are tailored to each patient's unique needs, targeting specific visual skills such as eye movement, focusing abilities, and binocular vision.
Types of Vision Therapy
- Oculomotor Therapy: This type of vision therapy focuses on improving eye movement and coordination. It includes exercises that help strengthen the eye muscles and enhance the ability to track moving objects accurately.
- Vergence Therapy: Vergence refers to the ability of the eyes to work together efficiently, especially when focusing on objects at different distances. Vergence therapy aims to improve binocular vision and depth perception through exercises that stimulate convergence (inward eye movement) and divergence (outward eye movement).
- Accommodative Therapy: Accommodation refers to the eye's ability to adjust focus for objects at varying distances. Accommodative therapy targets this skill, helping individuals improve their focusing abilities, particularly for near tasks like reading or using electronic devices.
- Visual Perceptual Therapy: Visual perception involves the brain's interpretation of visual information. Visual perceptual therapy aims to enhance skills such as visual memory, form recognition, and visual processing speed, which are crucial for tasks like reading comprehension and spatial awareness.
Get more detailed info on Vision Therapy here.
Benefits of Vision Therapy
- Improved Visual Function: By targeting specific visual skills, vision therapy can lead to enhanced eye movement, focusing abilities, and depth perception, ultimately improving overall visual function.
- Enhanced Academic Performance: For children struggling with reading or learning difficulties related to visual processing disorders, vision therapy can significantly improve academic performance by addressing underlying visual issues.
- Reduced Dependence on Corrective Lenses: In some cases, successful completion of vision therapy can reduce the need for strong prescription eyeglasses or contact lenses, as visual skills improve and reliance on optical aids decreases.
- Enhanced Sports Performance: Athletes can benefit from vision therapy to improve hand-eye coordination, visual tracking, and depth perception, leading to better performance in sports that require precise visual skills.
- Improved Quality of Life: Beyond academic or athletic pursuits, vision therapy can enhance daily activities such as driving, reading, and using electronic devices, leading to an improved quality of life for patients of all ages.
The Takeaway
Research in the field of vision therapy continues to advance, with studies demonstrating its effectiveness in treating conditions such as convergence insufficiency, amblyopia, and visual processing disorders. With ongoing advancements in technology and methodology, vision therapy remains a dynamic and effective approach to improving visual function and optimizing patient outcomes. As awareness of the benefits of vision therapy grows, more individuals are seeking out these specialized services to address their visual concerns and enhance their overall quality of life.
Share this blog post on social or with a friend:
The information provided in this article is intended for general knowledge and educational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. It is strongly recommended to consult with an eye care professional for personalized recommendations and guidance regarding your individual needs and eye health concerns.
All of Urban Optiks Optometry's blog posts and articles contain information carefully curated from openly sourced materials available in the public domain. We strive to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the information provided. For a comprehensive understanding of our practices and to read our full disclosure statement, please click here.