Exploring Eye-Related Cancers: Types, Symptoms, and Treatments
Read time: 5 minutes
Cancer is a complex and challenging disease that can affect various parts of the body, including the eyes. Eye-related cancers encompass a range of conditions that can impact vision and overall eye health.
Eye cancer, also known as ocular cancer, is rare, with only about 3,500 new cases diagnosed each year. It can be most treatable when discovered early through a dilated eye exam once a year. Eye cancer can affect the outer parts of the eye, such as the eyelid, or inside the eyeball, which is called intraocular cancer.
Understanding these cancers, their symptoms, and available treatments is crucial for early detection and effective management. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the types of eye-related cancers and how they can affect the eyes.
Differentiating Ocular Cancer from Intraocular Cancer
When discussing eye-related cancers, it's important to first differentiate between ocular cancer and intraocular cancer. Ocular cancer refers to any cancer that originates within the eye, affecting the various structures such as the retina, iris, or eyelids. This includes conditions like retinoblastoma, melanoma, and squamous cell carcinoma that develop within the eye itself.
On the other hand, intraocular cancer specifically refers to tumors that grow inside the eye, often originating from the tissues within the eye, such as the retina or iris. These tumors can be benign or malignant and may include conditions like intraocular melanoma or retinoblastoma.
The distinction between ocular and intraocular cancer lies in the location and origin of the cancerous cells. Ocular cancer encompasses a broader category of cancers affecting the eye as a whole, while intraocular cancer specifically denotes tumors that grow within the eye's internal structures. Both types require prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment to preserve vision and prevent further complications.
Types of Eye-Related Cancers
Eye-related cancers encompass a variety of conditions that can affect different parts of the eye. Notable types of eye cancers include:
- Retinoblastoma is a rare form of eye cancer that predominantly impacts young children, typically under the age of five. Its symptoms can manifest as a white glow in the pupil, crossed eyes, or redness in the affected eye. Treatment for retinoblastoma typically encompasses a combination of surgical procedures, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy, tailored to the severity and spread of the cancer within the eye.
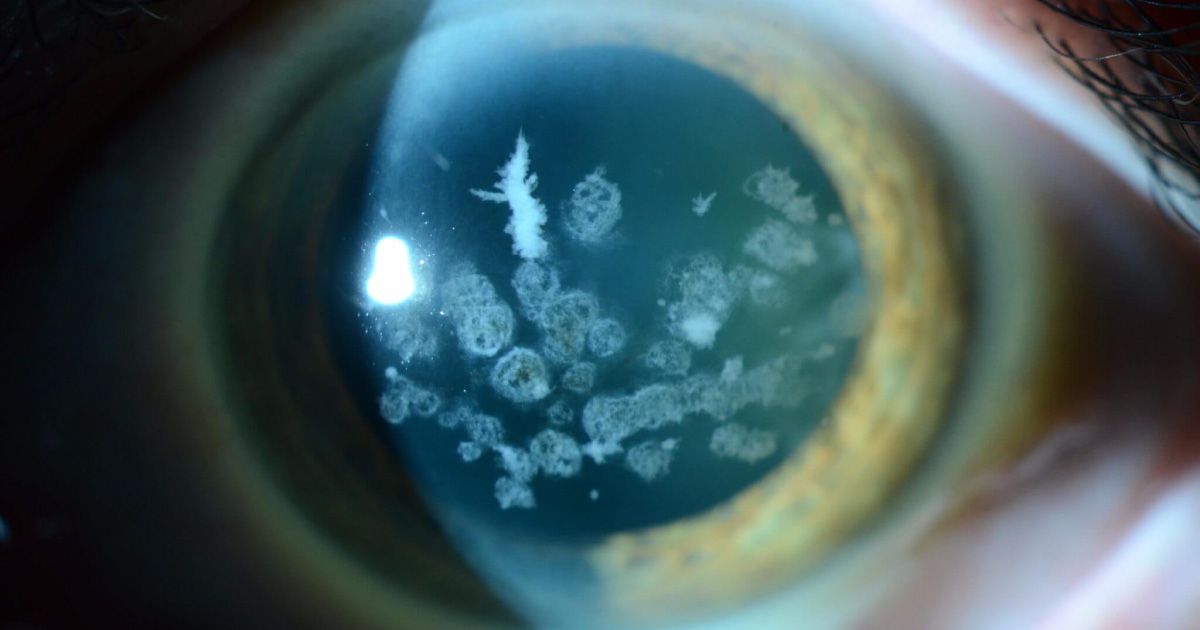
- Melanoma is another type of eye-related cancer that can occur, particularly in the uvea, which is the middle layer of the eye. Symptoms of ocular melanoma may include changes in vision, eye pain, or the appearance of dark spots within the eye. Treatment for melanoma of the eye may involve surgical intervention, radiation therapy, or targeted therapy to address the cancerous cells and preserve vision whenever possible.
- Lymphoma can also affect the eyes, either as primary ocular lymphoma or as part of systemic lymphoma. Symptoms of ocular lymphoma may include blurry vision, floaters, or eye redness. Treatment typically involves chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or radiation therapy, depending on the specific type and stage of lymphoma affecting the eye.
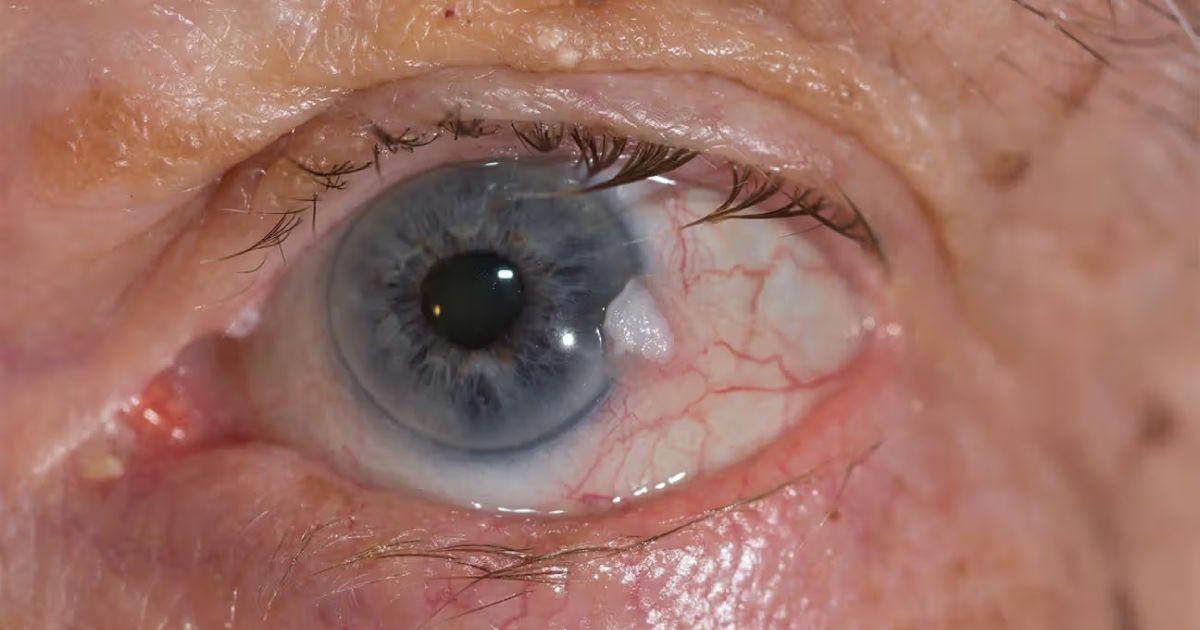
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma is a type of cancer that can develop on the surface of the eye or the eyelids. Its symptoms may include the presence of a growth on the eye or eyelid, persistent redness, or irritation. Treatment for squamous cell carcinoma often involves surgical removal of the cancerous cells, along with additional therapies as needed to prevent recurrence and preserve eye function.
- Intraocular Tumors are a category of eye-related cancers that can develop inside the eye, such as in the retina or iris. Symptoms may vary depending on the location and size of the tumor, ranging from vision changes to discomfort in the affected eye. Treatment options for intraocular tumors may include surgical removal, laser therapy, or targeted treatments aimed at managing the tumor and maintaining visual function as much as possible.
Understanding the different types of eye-related cancers and their respective symptoms is crucial for early detection, timely intervention, and effective management of these conditions to preserve vision and overall eye health.
Effects of Eye-Related Cancers
Eye-related cancers can have significant effects on vision and overall eye function. Depending on the type and stage of the cancer, individuals may experience:
- Vision changes, such as blurriness, double vision, or loss of vision.
- Eye pain or discomfort, especially if the cancer affects the structures within the eye.
- Changes in the appearance of the eye, including swelling, redness, or the presence of abnormal growths.
- Increased sensitivity to light or difficulty with bright lights.
- Challenges with eye movements or coordination, particularly if the cancer impacts the muscles or nerves controlling eye movements.
Early Detection and Prevention
Early detection plays a crucial role in effectively managing eye-related cancers. Regular eye exams are essential for detecting any abnormalities or changes in the eyes that may indicate a potential cancerous condition. Some preventive measures and tips include:
- Routine Comprehensive Eye Exams: Schedule regular comprehensive eye exams with an optometrist or ophthalmologist to monitor eye health and detect any issues early.
- Awareness of Symptoms: Be aware of common symptoms of eye-related cancers, such as vision changes, eye pain, or unusual growths on the eye or eyelids.
- Sun Protection: Wear sunglasses with UV protection and hats to shield the eyes from harmful UV rays, which can contribute to certain types of eye cancers.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco use, as these factors can impact overall health and reduce the risk of cancer.
Latest Treatments and Advances
Advancements in medical technology and treatment options have improved outcomes for individuals with eye-related cancers. Some of the latest treatments and approaches include:
- Targeted Therapies: Targeted therapies focus on specific molecular targets within cancer cells, allowing for more precise and effective treatment with fewer side effects.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy harnesses the body's immune system to target and destroy cancer cells, offering new hope for individuals with certain types of eye cancers.
- Minimally Invasive Surgeries: Advances in surgical techniques, such as robotic-assisted surgery and microsurgery, have made procedures safer and more precise, leading to better outcomes for patients.
- Genetic Testing: Genetic testing can help identify individuals at higher risk for certain eye-related cancers, allowing for proactive screening and early intervention.
The Takeaway
Eye-related cancers encompass a diverse range of conditions that can impact vision and eye health. By understanding the types of cancers, their effects, and available treatments, individuals can take proactive steps for early detection, prevention, and effective management. Regular eye exams, awareness of symptoms, sun protection, and staying informed about the latest advancements in cancer treatment are key factors in promoting eye health and overall well-being.
Don't delay in ensuring that your eye health is in tip-top shape. Early detection is key! Schedule a comprehensive eye exam today and take proactive steps towards maintaining clear vision and overall well-being.
Share this blog post on social or with a friend:
The information provided in this article is intended for general knowledge and educational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. It is strongly recommended to consult with an eye care professional for personalized recommendations and guidance regarding your individual needs and eye health concerns.
All of Urban Optiks Optometry's blog posts and articles contain information carefully curated from openly sourced materials available in the public domain. We strive to ensure the accuracy and relevance of the information provided. For a comprehensive understanding of our practices and to read our full disclosure statement, please click here.